|
Hi there! I am a PhD Candidate in the Computer Science & Engineering (CSE) division at the University of Michigan, advised by Prof. Stella X. Yu. I earned my B.S. in CSE from the Ohio State University, Summa Cum Laude. My research currently focuses on vision-language foundation models for context-aware, visually grounded,and agentic perception. My long-term pursuit is developing perception for embodied interaction with the physical world. I am also motivated by applications that connect AI with other disciplines. Email / Google Scholar / Twitter / LinkedIn |

|
Research |

|
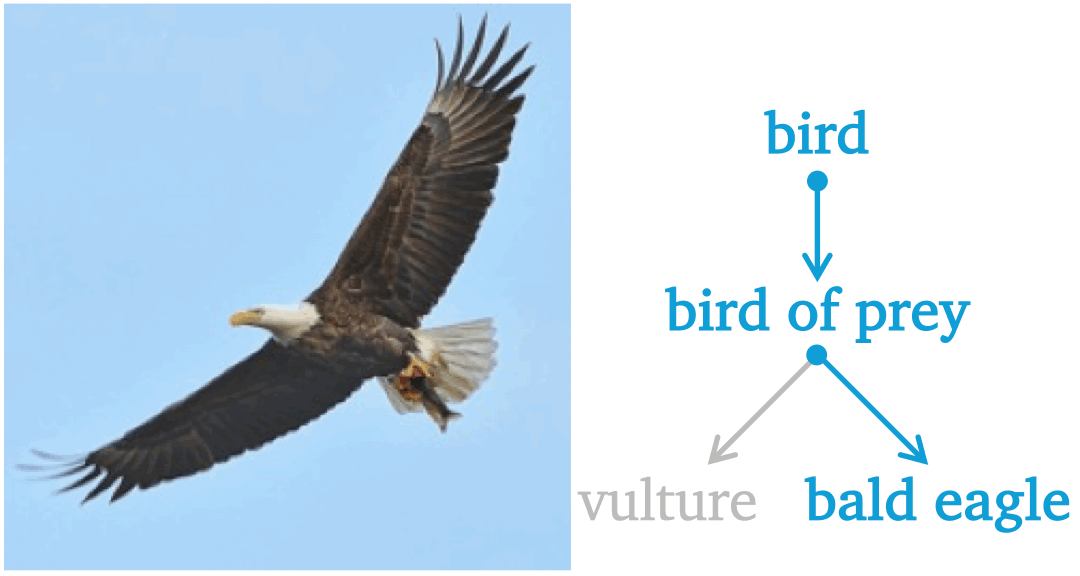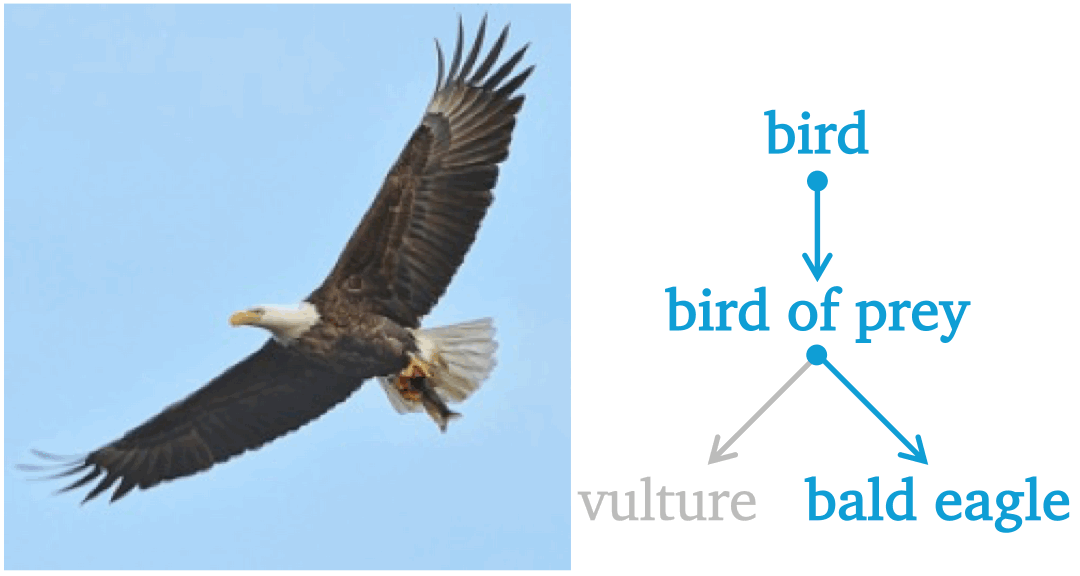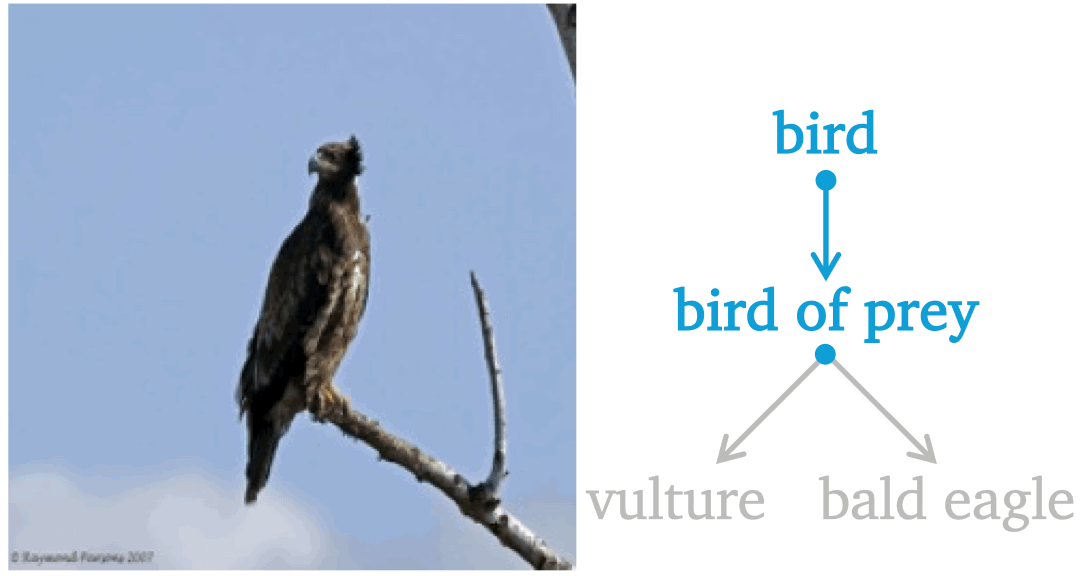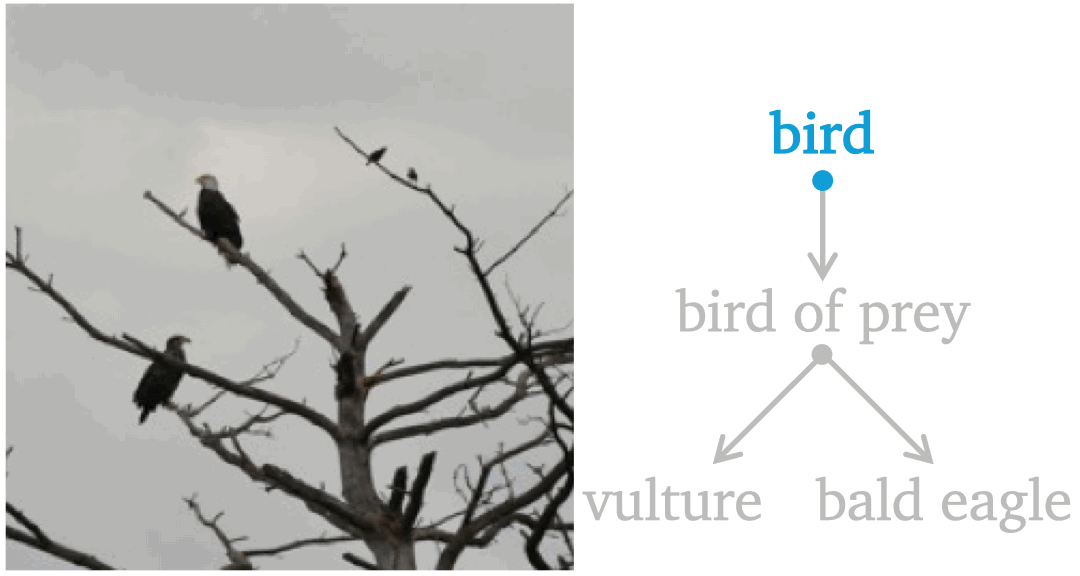
Aligning Forest and Trees in Images and Long Captions for Visually Grounded Understanding
Byeongju Woo, Zilin Wang, Byeonghyun Pak, Sangwoo Mo, Stella X. Yu In submission preprint / code We propose CAFT, a hierarchical image-text representation framework that aligns visual and linguistic hierarchies from long captions without region-level supervision. Trained on 30M image-text pairs, CAFT achieves state-of-the-art results on six long-text benchmarks, demonstrating the power of hierarchical alignment for fine-grained visual-language understanding and visual grounding. |
|
Free-Grained Hierarchical Recognition
Seulki Park, Zilin Wang, Stella X. Yu CVPR, 2026 preprint / code We introduce ImageNet-F, a large-scale benchmark with mixed-granularity labels reflecting real-world annotation variability. Using this dataset, our free-grain learning framework leverages semantic and visual guidance to improve hierarchical image classification under heterogeneous supervision. |

|
Open Ad-Hoc Categorization with Contextualized Feature Learning
Zilin Wang*, Sangwoo Mo*, Stella X. Yu, Sima Behpour, Liu Ren CVPR, 2025 preprint / webpage / poster / code Ad-hoc categories are created dynamically to achieve specific tasks based on context at hand, such as things to sell at a garage sale. We introduce open ad-hoc categorization (OAK), a novel task requiring discovery of novel classes across diverse contexts, and tackle it by learning contextualized visual features with text guidance based on CLIP. |
TeachingUM EECS 442: Computer Vision
UM EECS 542: Advanced Topics in Computer Vision
UM EECS 598: Action & Perception
UM SI 670: Applied Machine Learning
|
Academic Service & Outreach
|
|
Design and template code from Jon Barron |
